Many years back, smartphones were considered a luxury. Yes, we are referring to the time when smartphone users had to pay even for incoming calls 🙂 Fast-forward now, smartphones have become a necessity. Banking, shopping, bill payments, etc. can now be done at the click of a button.
The smartphone revolution is reality and its growth can be attributed to the availability of affordable handsets and soaring growth of mobile internet (3G and 4G). As a matter of fact, 5G will further propel the staggering growth of mobile phones!
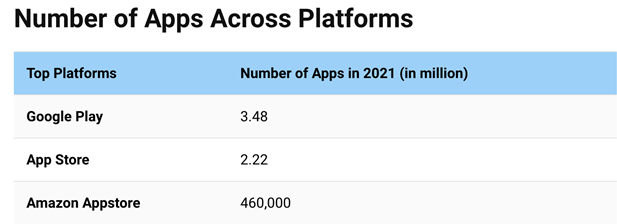
As per 2021 reports[1], there are close to 3.8 billion smartphone users in the world. Close to 21 percent[2] millennials open 50+ mobile apps in a day. Though the mobile app space is over-crowded with apps ranging in different categories, there still lies an opportunity to flourish if the app functions as per the user expectations.
Source
Since consumers have a lot of choices when it comes to mobile applications, it is important to invest in app development and testing so that a top-quality app can be released in the respective mobile app stores. Mobile app testing must be an indispensable part of the mobile app strategy.
The first & foremost step in building a killer mobile app testing strategy is understanding the various types of mobile app testing methodologies (or approaches). This will help in prioritizing the app testing approaches that matter the most for your application.
What is Mobile Application Testing?
Mobile application testing (or mobile app testing) is the process of testing the mobile app from functionality and usability point of view on different browsers, devices, and device viewports.
As there are umpteen combinations of browsers, browser versions, and device viewports; it is important to prioritize the ones that are being used in the target market. Mobile app testing encompasses testing of a wide range of applications – native apps, responsive apps, and hybrid apps.
By the end of the rigorous mobile app testing cycles, you would have a fully functional and well-performing mobile app that can be released to the target users. Mobile app testing services offered by proven outsourced QA vendors like KiwiQA can also be leveraged to accelerate the delivery cycles of the app.
Now that we have covered the basics of mobile app testing, let us deep dive into the major types of mobile testing.
Also Read – Checklist To Test Your Mobile App Successfully
Different Types of Mobile App Testing
Here are the major types (or forms) of mobile app testing:
1. Geolocation and Localization Testing
There are a number of mobile applications that are localized for a particular geography (or locale). However, a large number of applications are built for a global user-base. For example, an e-commerce application might only be shipping in a few countries but there is a high possibility that it might be available for download for the global user base.
Geolocation testing of mobile apps helps in verifying the functionalities of the app when it is accessed from different geographies. When apps appeal to a global user base, the features and/or content also has to be localized as per the particular locale. The app must also adhere to the local laws and regulations.
Localization testing of mobile apps is important for ensuring that the content, features, and other aspects of the app are inline with the requirements of the local audience. Apps that are tested thoroughly for geolocation and localization perform much better when compared to the ones that are not tested on those fronts.
2. Usability Testing
Though users download the required app for its functionalities, they stick around for the user experience. The user-flow in the app must be simple so that users are able to navigate in the app with ease. Also, the app must be super-functional so that users do not encounter any problems.
This is why end-to-end tests on real devices becomes necessary since it helps in testing the app from an end-user’s perspective. The usability tests have to be conducted on real devices that are being used by the users in the target market.
The app must also be tested for responsiveness and intuitiveness in usability testing.
3. Security Testing
Close to 81 percent users[3] are willing to uninstall the app if there is any compromise on security and privacy fronts.
There is a myth that data security is only applicable for mobile apps where the users have to deal with monetary transactions. In fact, data security and privacy are extremely important for all mobile applications.
End-to-end security testing must be conducted to make sure that the app is not only functional but also adheres to all the required security standards.
4. Performance Testing
Performance tests of mobile applications are important to ensure that the app’s performance does not deteriorate under different working conditions. Battery consumption, memory consumption, app sluggishness, app load times, and other such parameters must be measured for checking the app’s performance.
Device performance, network performance, app recovery, etc. are some of the important aspects that must be covered in performance testing. Since most of the mobile applications involve interactions with the server, it is also important to consider the overall time taken to fulfill the app requests.
Also Read – Load Testing vs. Performance Testing vs. Stress Testing
5. Memory Leak Testing
For starters, memory leak in a software is caused when a dynamically allocated memory block is not freed using the required APIs. Mobile apps can start crashing at random places if there are memory leaks since the dynamic memory chunk is not available for allocation.
As a part of functional testing, memory consumption must be monitored on a regular basis. Android Monitor is one of the widely used tools that offers CPU profiling, memory profiling, network profiling, and energy profiling.
The tool can also be used for benchmarking your mobile app vis-a-vis other similar applications.
On the whole, memory leak testing is performed by running the app on different configurations of mobile devices. This helps in optimizing the app so that it works efficiently on the target mobile devices.
Apart from the above testing types, mobile applications are also tested for speed. App load and app unload times are some of the parameters that can be tracked in speed testing. If the app (or website) is taking more than 3 seconds to load, it is time to optimize the app load time.
Conclusion
Mobile app testing has become an integral part of the mobile app strategy. Apart from app development, companies must also focus on app testing so that a fully functional app is released in the market.
The mobile testing types discussed in the blog will come in handy when devising the testing strategy. Whether you use the manual testing or automated testing, app testing must be performed on real devices since the apps would be used on real devices (and not on emulators/simulators).










